कक्षा 6 विज्ञान पाठ 2 वस्तुओं के समूह बनाना के प्रश्न उत्तर अंग्रेजी में
Latest NCERT Solutions 2024: Class 6th Science Chapter 2 Sorting Materials into Groups Notes in English | EDU-Favor
All things are made of one or more materials. The same thing can also be made of different materials.
It may be man-made or naturally occurring. Materials can be classified on the basis of many criteria. The sorting of objects into groups with each group having its own characteristics is called the classification of objects.
The substances can also be grouped by the similarity of the materials used to make them.
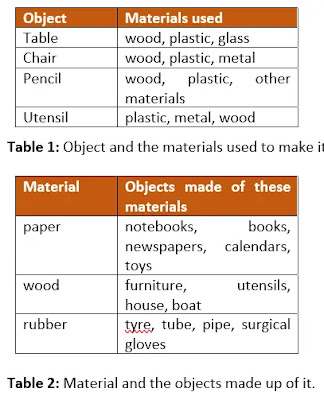
Table 1 shows the object and the materials used to make it.
Table 2 shows the material and the objects made by it.
Table 3 shows a single object made up of different types of materials..
Classification of Materials
Classification of materials is based on the similarities and differences between different materials. It has the following advantages:
It makes it easier and convenient to locate a variety of materials and to work with them.
It also helps in better understanding of materials. This is because if we know the properties of any one member of the group, we can get an idea of the properties of the other members of the same group.
Materials can be classified on the basis of the following properties:
Appearance
The appearance varies from one material to the other. Colour, texture, roughness and other parameters contribute to the appearance of materials. Materials with a shiny surface: are called lustrous (gold, silver, copper), whereas those which have a dull appearance are called non-lustrous (paper, cardboard, chalk),
Lustre
Some materials are lustrous(shiny) such as metals. While others are not shiny, The metals can lose their shine because of the presence of rust on them.
Hardness and Softness
Materials which cannot be easily compressed, cut, bent (moulded) or scratched are called hard materials. Examples: Iron, steel, wood, stone.
Materials which can be easily compressed, cut, bent (moulded) or scratched are called. soft materials. Examples: Sponge, cotton, wax.
Transparency
- Some substances that allow us to see pass through them are called transparent substances. The light can easily pass through them. The common examples of transparent objects are air, glass and some plastics.
- The objects that allow us to see but not clearly through them are called translucent objects. The examples of translucent objects are butter paper, tissue paper and thin plastic etc.
- The objects that do not allow us to see pass through them are called opaque objects. When the light falls on an opaque object, it does pass through it, meanwhile, it forms a shadow. Some examples of opaque objects are wood, human, stone and trees.
Solubility in water:
- A solution is a mixture of homogeneous (same components) or heterogeneous(different components).
- The material that is present in a small amount in a solution is called the solute. The solute can be dissolved or cannot be dissolved in a solution. For example, sugar can be dissolved in the water, but pieces of rock cannot.
- The solute that can be dissolved in a solution is called soluble substances. While some other substances that are not dissolved in a solution called insoluble substances.
- If the mixture of liquids successfully mix then it is called miscible liquids. While the liquids that do not mix with each other are called immiscible liquids.
Texture
- The feeling of roughness and smoothness while touching any object is called its texture.
- The smooth objects have plane surfaces and no bumps or ridges. For example, flowers and baby's skin etc.
- The rough objects have bumps or ridges and irregular surfaces. For example, tree-bark.
Conductivity
The substances that pass the electricity completely are called good conductors. For example, metals.
The substances that pass the electricity partially are called poor conductors. For example, graphite.
The substances that do not pass the electricity are called insulators. For example, wood.
Density and floatation
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
- The objects that have lower density than the water can float on it. For example, ice.
- The objects that have higher density than the water sink to it. For example, metals.
Malleability
It is a property of substances that can be changed into thin sheets while beating up. For example, metals like gold and silver are beaten up into thin sheets with a hammer.
Malleable Definition:- Malleability is the ability of a substance to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets.
Ductility
It is a property of metals that allow them to change into wires. For example, the filament of an electric bulb is made up of tungsten metal.
Matter
Anything which occupies mass and space is called matter. All the substances present in the universe are made up of matter.
Composition of matter:- Many atoms or a few atoms linked together to form matter. The smallest unit of a matter is called an atom. The same atoms linked together to form a molecule.
The short description of element and compound is given below:
Compound:- Diffrent types of atoms linked togather. The smallest particle that possesses the same property is it's molecules.
Elements:- Same atoms linked togather. The smallest particle that possesses the same property is it's atoms.
States Of Matter
The existence of a matter in different forms is known as states of matter.
There are three states of matter:
a) Solid State:- The particles of the solid-state substances are closely packed.
- The intermolecular force of attraction between the particles in very high.
- The particles are fixed at their places, only vibrate if they get higher energy.
- The solid state objects have definite shape and size.
- They also have definite volume.
b) Liquid State:- The particles of liquid have spaces between them.
- The intermolecular force of attraction is high but not as the particles of solid.
- The particles of liquid are continuously moving in random directions, and while moving, they collide with each other.
- The liquid substances take definite shape in a container.
- They have definite volume.
c) Gas State:- The particles of gaseous state are loosely packed.
- The intermolecular force of attraction is very low.
- The particles can move freely in any direction.
- They do not have definite shape, size, and volume.
- They can be compressed in a cylinder. For example, Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
कक्षा 6 विज्ञान अध्याय 2 एनसीईआरटी समाधान 2024 – वस्तुओं के समूह बनाना नोट्स | NCERT New Pattern 2024: Class 6th Science Chapter 2 Sorting Materials into Groups Notes |
Opacity
The quality or state of a body that makes it impervious to the rays of light.
- Materials through which we can see clearly are called transparent materials. Examples: Glass, air.
- Materials through which we can see but not clearly are called translucent materials. Examples: Oiled paper, ground glass.
- Materials through which we cannot see at all are called opaque materials. Examples: iron sheet, brick wall.
कक्षा 6 विज्ञान अध्याय 2 एनसीईआरटी समाधान 2024 – वस्तुओं के समूह बनाना नोट्स | NCERT New Pattern 2024: Class 6th Science Chapter 2 Sorting Materials into Groups Notes | EDU-Favor




Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.